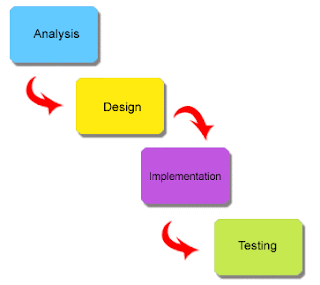
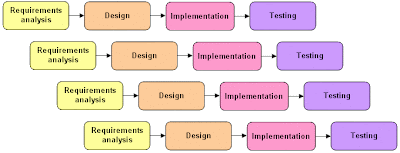
Definition:-A frame-work that describe the activities performed at each stage of a software development project, It is a logical systematic process used to develop software and information systems through planning, analysis, design, implementation and support. It is an approach that allow for System development to be a lot simplified and easy, less rigid and achieve Stability.
There are five Phases to the software Development life cycle:-
1) Planning
2) Analysis
3) Design
4) Implementation
5) Maintenance
S.D.L.C
- Planning- The initial phase starts by defining the need. The purpose of the planning phase is to identify clearly the nature and scope of the business opportunity or problem by performing a preliminary investigation. This entails investigating their current system and what they hope to have in the future.
- Analysis- In the analysis phase we get further information about what they want and build more in-depth models of what they can expect to achieve with their new system. Requirement for the software are documented and reviewed with the customer.
- Design- when the project really starts to take form, We Engineers plan out all the inputs, outputs, interfaces, processes for the project and create the system design specification from this data. The requirements translated into representation of the Software that can be assessed for quality before coding begins.
- Implementation-There are three stage of implementation a)coding : In this process design translated into a machine-readable form & if design is performed in a detailed manner, code generation can be accomplished mechanistically. b)testing : After coding team will make a prototype model to ensure that System will meet the needs of customer. c)Installation : Then after everyone Satisfied that the System is ready they will install the product and convert it into customer existing format.
- Maintenance-It refers to the support phase of software development. In this final phase, the team maintains the system and updates it as necessary to keep up to date with its environment. It focuses on change associated with error correction, changes due to enhancements brought about by changing customer requirements.
SDLC Model:-
Definition:-An abstract representation of a process describe the activities performed at each stage of a software development project .
Ø Waterfall Model
Ø RAD Model
Ø Iterative Development Model
Ø The Incremental Development Model
Ø Spiral Model
Ø The Parallel or Concurrent Development Model
Waterfall Model:-
Definition:-This Model also called Linear sequential Development Model, this model suggest a systematic Sequentially approach to Software development that begins at the System level and progress through analysis, design, coding ,testing , and support .It has a lock step fashion, where a stage cannot begin unless the preceding stage is completed.
v Analysis- Defines needed information, function, behavior, performance and interfaces.
v Design- Data structures, software architecture, interface representations, procedural details.
v Implementation- Code generation, database, user documentation, testing.
q NOTE-In waterfall model after all phases Documentation done.
Benefits-
• Easy to understand, easy to use.
• Appropriate for small Software.
• Provide lots of documentation for each phase which is very important for future.
• Important for those system where each phases is considered as discrete phase.
• Good for management control (plan, staff, track).
• Works well when quality is more important than cost or schedule.
• Milestone are well understood.
• Sets requirement stability.
Limitation-
• Not appropriate for large Software.
• Requires lots of documentation which is time consuming.
• When any changes need than we have to go to initial phase.
• Deliverables created for each phase are considered frozen – inhibits flexibility.
• Can give a false impression of progress
• Does not reflect problem-solving nature of software development – iterations of phases
• Integration is one big bang at the end.
• Little opportunity for customer to preview the system (until it may be too late).
RAD Model:-
v Definition- Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a software development methodology. It is a development lifecycle designed to give much faster development and higher-quality results than those achieved with the traditional lifecycle. It is designed to take the maximum advantage of powerful development software that has evolved recently.”
- The RAD approach encompasses the following phases:-
Ø Business Modeling
Ø Data modeling
Ø Process Modeling
Ø Application Generation
Ø Testing & Turnover
RAD approaches following phases:
Business model-Here we try to find answer to question like what information is generated? Who generate it? Etc.
Data modeling-It is a method used to define and analyze data requirements needed to support the business processes of an organization.
Process modeling- Process models are processes of the same nature that are classified together into a model.
Application generation-A series of occasional musings on architecting, securing, optimizing and generating web based applications.
Testing & Turnover-Many of the program components have already been tested so this reduce overall testing time.
Benefits:-
• Due to factors like iterative development more client satisfaction. Clients are involved from beginning to end.
• If done right you work out more initial requirement bugs before installation.
• You reduce the moving target syndrome.
• Focalizing data into one view instead of many screens.
• RAD's usual focus is on high return developments. Usually related to the financial sectors of the business. In my experience 10-1 payback in first year is easily obtainable.
• Reusable objects make future developments even faster.
• Time boxing really allows us to focus on deliverable components.
Drawbacks:-
• Not all types of application are appropriate for RAD.
• If the system cannot be properly modularize, building the component necessary for RAD will be problematic.
• RAD is not appropriate when technical risk are high.
• It is like college development projects. we would produce something that performed the required functions, looked good, but usually was not the best quality. Due to time constraints we submit what we have accomplished and take credit.
• The client usually gets a shell of what they want with several sections to be added in future projects(if we get to them).
• Initial project requirements are usually under estimated.
• Client expectations go through the roof. Suddenly they can't wait six months. Even though before RAD we told them two years or more.
Iterative Development Model:-
Definition:-Iterative development is at the heart of a cyclic software development process developed in response to the weaknesses of the waterfall model. It starts with an initial planning and ends with deployment with the cyclic interactions in between.
Benefits:-
• Advantage of this approach is that it can result in better testing because testing each increment is likely to be easier than testing the entire system as in waterfall model.
• The increment model provide feedback to the client.
• It is useful for determining the final requirement of the System.
• This project control list gives an idea of how far the project is at any given step from the final System.
• At each step, extensions and design modifications can be made.
• Useful for testing the system within the development in starting.
Drawbacks:-
• In a customized software development, where the client has to essentially provide and approve the specifications, it is not always clear how this process can be applied.
• Practical problem with this type of development project, comes in generating the business contract-how will the cost of additional feature be determined and negotiated.
• In the latter steps, the design would have stabilized and there is less chances to redesign.
The Incremental Developmental Model:-
Definition:-A software development technique in which requirement definition, design, implementation, and testing occur in an overlapping, iterative manner, resulting in incremental completion of the overall software product.
Benefits:-
• Early increment can be implemented with fewer people.
• Develop high-risk or major functions first.
• Each release delivers an operational product .
• Customer can respond to each build.
• Uses “divide and conquer” breakdown of tasks.
• Lowers initial delivery cost .
• Initial product delivery is faster.
• Risk of changing requirements is reduced.
Drawbacks:-
• A major system might require the availability of new hardware.
• Requires good planning and design
• Requires early definition of a complete and fully functional system to allow for the definition of increments
• Well-defined module interfaces are required (some will be developed long before others)
• Total cost of the complete system is not lower
Spiral Model:-
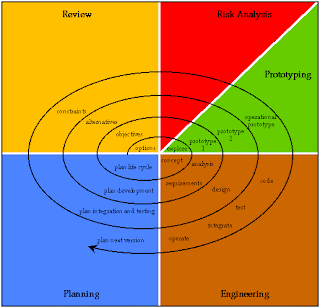 Definition
Definition:-The spiral model is a software development process combining elements of both design and prototyping-in-stages, in an effort to combine advantages of top-down and bottom-up concepts. This model couples the iterative nature of the prototyping with the control and Systematic approach of linear model.
Benefits:-
• Provides early indication of insurmountable risks, without much cost
• Users see the system early because of rapid prototyping tools
• Critical high-risk functions are developed first
• The design does not have to be perfect
• Users can be closely tied to all lifecycle steps
• Early and frequent feedback from users
• Cumulative costs assessed frequently
Limitation:-
• Time spent for evaluating risks too large for small or low-risk projects
• Time spent planning, resetting objectives, doing risk analysis and prototyping may be excessive
• The model is complex
• Risk assessment expertise is required
• Spiral may continue indefinitely
• Developers must be reassigned during non-development phase activities
• May be hard to define objective, verifiable milestones that indicate readiness to proceed through the next iteration
The parallel or Concurrent Development Model:-
Definition:-The concurrent process model defines a series of event that will trigger transition from state to state for each of the software engineering activities. This model is used for designing and developing of client server application.
Component based Development Model:-
This model compose application from prepackage software component called class. Classes created in past s/w project are stored in a class library and the s/w development is done on the basis of reusability by reusing the class from class libraries. The component based development model leads to software reuse, and reusability provides software engineers with a number of measurable benefits although it is very much dependent on the robustness of the component library.